Top 10 Virtual Machine Software and Why Each Developer Should Learn VM
Reading time: 4 minutes
If you are a developer, you may have heard of virtual machines. Virtual machines have become an integral part of modern software development, not just a nice-to-know but a skill each developer should master. Whether you are building applications, testing across environments, or experimenting with new tools, VMs deliver a safe, flexible, and cost-effective space to work without risking your main system.
In today’s rapidly evolving era, teams require environments that can be created, destroyed, or replicated within minutes. That’s where virtual machine software comes in. With just a few clicks, you can spin up a test server, try a different operating system, and run a sandboxed environment, all on a single physical machine.
This post is going to explain the top 10 virtual machine software used across the industry and tell why each developer should learn VM technology. Understanding these tools not only increases productivity but also enhances your ability to troubleshoot, deploy, automate, and innovate in a cloud-driven tech landscape.
What is a Virtual Machine?
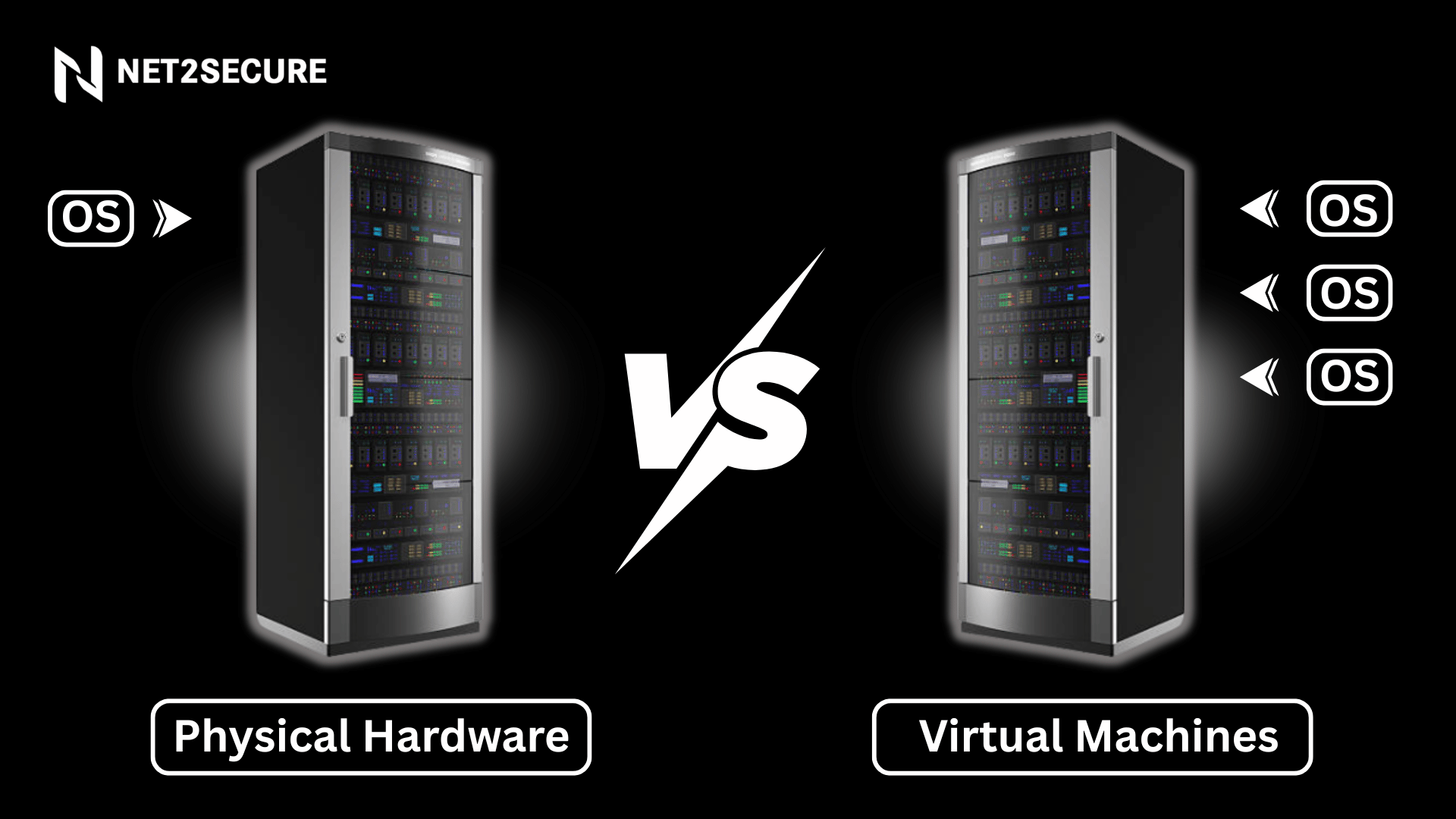
The term virtual machine refers to a computer resource that uses software rather than a physical computer to run programs and deploy applications. One or more virtual guest machines run on a physical “host” machine. Each virtual machine runs its own operating system and functions separately from the other VMs, even when they are all operating on the same host. It means a virtual macOS machine can run on a physical PC.
Virtual machine technology is primarily used for several use cases across on-premises and cloud environments. Recently, public cloud hosting services have been using virtual machines to offer virtual application resources to different users at once, for even more affordable and flexible compute.
Understanding Virtual Machine Software
Virtual machine software is a technology that creates virtualized computer systems within a physical host machine, enabling different operating systems to operate simultaneously on the same hardware.
Top 10 Virtual Machine Software Each Developer Should Master
-
VMware Workstation Pro
-
Oracle VM VirtualBox
-
Parallels Desktop
-
Microsoft Hyper-V
-
QEMU
-
Docker Desktop
-
Citrix Hypervisor (XenServer)
-
Red Hat Virtualization (RHV)
-
Proxmox VE
-
Vagrant
VMware Workstation Pro
The Enterprise Standard
VMware Workstation Pro remains the gold standard for professional virtualization, delivering exceptional stability and feature depth.
Key Features:
- Support for 100+ guest operating systems
- Modern 3D graphics with DirectX 11 and OpenGL 4.1
Oracle VM VirtualBox
The Free Powerhouse
VirtualBox adjusts virtualization with its completely free, open-source approach that doesn't compromise on crucial features.
Key Features:
- Cross-platform support, Windows, macOS, Linux
- Guest Additions for better integration
Parallels Desktop
The Mac Virtualization Champion
Parallels Desktop 20 arrived in September 2024, bringing support for macOS Sequoia and its new features, like AI-powered Apple Intelligence features.
Key Features:
- Coherence mode for effective Windows-Mac integration
- Touch Bar support for Windows applications
Microsoft Hyper-V
The Windows Native Solution
Built into Windows Pro and Enterprise editions, Hyper-V delivers solid OS integration and enterprise-grade features.
Key Features:
- Type-1 hypervisor for improved performance
- Live migration capabilities
QEMU
The Versatile Open-Source Emulator
QEMU offers both complete system emulation and virtualization capabilities with extensive architecture support.
Key Features:
- Support for various CPU architectures (x86, ARM, RISC-V)
- KVM acceleration on Linux
Docker Desktop
The Container Revolution
While technically, containerization instead of traditional VMs, Docker has transformed application deployment and development.
Key Features:
- Lightweight container-based virtualization
- Kubernetes integration
Citrix Hypervisor (XenServer)
The Enterprise Virtualization Platform
XenServer, earlier known as Citrix Hypervisor, started life as an open-source project, and to this day, it remains free to download and install.
Key Features:
- Type-1 bare metal hypervisor
- Live migration and high availability
Red Hat Virtualization (RHV)
The Open-Source Enterprise Solution
Built on KVM and QEMU technologies, RHV offers enterprise-grade virtualization for Linux environments.
Key Features:
- KVM-based hypervisor technology
- Self-hosted engine architecture
Thus, virtual machines have developed a crucial part of modern development, allowing teams to build, test, and deploy software with exceptional flexibility. Whether you are operating a Windows application on macOS, experimenting with a new Linux distribution, creating isolated test environments, or managing large-scale enterprise workloads, VM software makes it possible without investing in additional hardware.